Human-in-the-Loop (HITL)
An AI system where humans actively participate in training and decision-making to ensure accuracy, safety, and ethical outcomes by combining human judgment with machine speed.
What Is Human-in-the-Loop (HITL)?
HITL integrates human intelligence directly into AI and ML workflows. Humans participate at key stages—labeling training data, tuning models, validating outputs, and making or overriding decisions. This feedback loop leverages human expertise for context, judgment, and ethical reasoning, complementing the speed and scale of automation.
Key source:
- IBM: What Is Human In The Loop (HITL)?
- Stanford HAI: Humans in the Loop
- MIT Press: Data Science and Engineering With Human in the Loop
HITL is distinct from “human-on-the-loop” (where humans monitor and intervene as needed) and “human-out-of-the-loop” (where AI operates autonomously).
Why Use Human-in-the-Loop?
HITL is essential when:
- AI alone cannot handle ambiguity or high-stakes decisions.
- Regulations require human oversight (e.g., EU AI Act).
- Trust, transparency, and accountability are non-negotiable (healthcare, finance, legal, safety-critical sectors).
- Edge cases and bias pose risks that pure automation cannot address.
Example:
When processing invoices, AI models extract standard fields, but ambiguous handwriting or unusual layouts require human review. Corrections are fed back into the system, improving future accuracy (Google Cloud).
How Does Human-in-the-Loop Work?
Core Workflow Steps
Data Annotation:
Humans label or annotate data to provide ground truth for ML training. This is crucial for tasks with subjectivity, ambiguity, or domain knowledge (e.g., medical images, spam detection, computer vision).Model Training & Tuning:
Annotated data is used to train the AI model. Human experts adjust parameters, evaluate performance, and mitigate bias or errors.Evaluation & Validation:
Human reviewers assess model outputs for quality, relevance, safety, and compliance. Edge cases or uncertain predictions are flagged and corrected.Feedback & Retraining:
Human corrections and judgments are incorporated into the training data, refining the model in a continuous feedback loop.Decision Oversight:
In production, AI handles routine cases, escalating ambiguous or high-risk decisions to humans.
More on HITL workflows:
HITL in Action: Example Domains
- Supervised Learning: Humans label training data (images, text) for correct classification.
- Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF): Human feedback trains reward models for desired agent behaviors.
- Active Learning: The system identifies uncertain cases and requests human input only when needed, optimizing resources.
- Agentic Systems: HITL is critical where AI agents can trigger workflows, access sensitive data, or make impactful decisions (Permit.io).
Example Use Cases
1. Intelligent Document Processing
AI extracts information from forms or contracts. Humans validate or correct outputs on ambiguous fields (e.g., unclear handwriting), and corrections retrain the model.
2. Healthcare Diagnostics
AI analyzes medical scans. Clinicians review flagged anomalies, enhancing accuracy and regulatory compliance.
3. Content Moderation
AI flags potential violations (hate speech, nudity, misinformation). Human moderators review edge cases for nuance and context.
4. Customer Service
AI chatbots handle routine queries. Humans intervene for complex or sensitive cases, improving satisfaction and escalation.
5. Autonomous Vehicles & Robotics
Self-driving cars and robots require HITL for unexpected scenarios or failures.
6. Finance & Compliance
Algorithmic trading systems and legal tech require human review for regulatory compliance and anomaly detection.
More success stories:
Main Roles of Humans in HITL
- Annotators: Label and curate data for training and evaluation.
- Domain Experts: Provide subject matter expertise for edge cases and ambiguous decisions.
- Model Validators: Evaluate outputs for quality, compliance, and safety.
- Supervisors/Oversight: Monitor operations, intervene, and document decisions for transparency and auditability.
Benefits of Human-in-the-Loop
1. Improved Accuracy and Reliability
Humans catch errors, ambiguous cases, and edge scenarios, enabling continuous improvement.
2. Bias Mitigation and Ethical Oversight
Humans spot and correct biases in data and algorithms, supporting fairness.
3. Transparency and Accountability
Human participation provides audit trails, supporting explainability and regulatory compliance.
4. Regulatory Compliance
Many regulations require human oversight in high-risk AI applications.
5. Operational Efficiency
Delegating routine cases to AI and reserving humans for exceptions ensures scale and quality.
Drawbacks and Challenges
1. Scalability and Cost
Human annotation, validation, and oversight can be resource-intensive. Scaling requires workflow design and tooling.
2. Human Error and Inconsistency
Humans introduce bias, fatigue, and subjectivity, affecting data quality.
3. Privacy and Security
Human access to sensitive data raises privacy concerns and risk of data leaks.
4. Bottlenecks and Delays
Without automation, HITL steps can become bottlenecks as data volumes grow.
HITL vs. Human-on-the-Loop vs. Human-out-of-the-Loop
- HITL: Humans embedded in the feedback cycle, actively label, validate, and correct.
- Human-on-the-Loop: Humans supervise and can intervene but are not part of every operation.
- Human-out-of-the-Loop: AI acts fully autonomously post-deployment.
Application choice depends on risk, required accuracy, and regulatory needs.
HITL Design: Best Practices
Targeted Human Input:
Focus humans on ambiguous, low-confidence, or high-risk tasks via active learning and triage.Iterative Feedback Loops:
Continuously retrain models with human corrections for incremental improvement.Role-Based Workflows:
Assign clear roles (annotator, reviewer, supervisor) with access controls.Tooling and Automation:
Use HITL platforms (e.g., SuperAnnotate, Encord) for workflow management, analytics, and audit trails.Compliance and Documentation:
Maintain logs and audit trails for regulatory adherence.Quality Control:
Use “golden sets” of test cases for consistent benchmarking.Continuous Monitoring:
Track deployed models for drift and escalate new edge cases for review.
Real-World Case Studies
Document Processing:
Logistics firm increased invoice extraction accuracy from 82% to 98% with HITL (Parseur).Healthcare Imaging:
Combining AI and clinician review raised diagnostic accuracy to 99.5% (Nexus Frontier).Sales Lead Qualification:
AI chatbots filter leads, humans handle nuanced cases, boosting close rates (Parseur).Content Moderation:
AI detects ~88% of harmful content, but 5–10% of cases need human review (SEO Sandwich).
References & Further Reading
- IBM: What Is Human In The Loop (HITL)?
- SuperAnnotate: What is Human-in-the-Loop?
- Encord: Human-in-the-Loop in AI
- Parseur: Human-in-the-Loop AI
- Google Cloud: HITL
- Permit.io: HITL Best Practices & Use Cases
- Stanford HAI: Humans in the Loop
- EBSCO: HITL
- EU AI Act
- Nexus Frontier: HITL in healthcare
- Tely.ai: Benefits of HITL
Summary Table: HITL at a Glance
| Aspect | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Human involvement in AI/ML lifecycle, including training, tuning, oversight | Humans label data for computer vision |
| Key Benefits | Accuracy, bias mitigation, transparency, compliance, efficiency | 99.9% accuracy in document processing |
| Challenges | Scalability, cost, human error, privacy, bottlenecks | Annotating millions of images |
| Core Roles | Annotator, expert, validator, supervisor | Clinician reviews flagged scans |
| Best Practices | Targeted input, feedback loops, robust tooling, compliance, monitoring | Active learning to focus annotation |
| Industries | Healthcare, finance, moderation, autonomous vehicles, customer service, legal tech | HITL for chatbot escalation |
Visual Resources
- HITL Workflow Diagram:

- HITL Use Case Infographic:
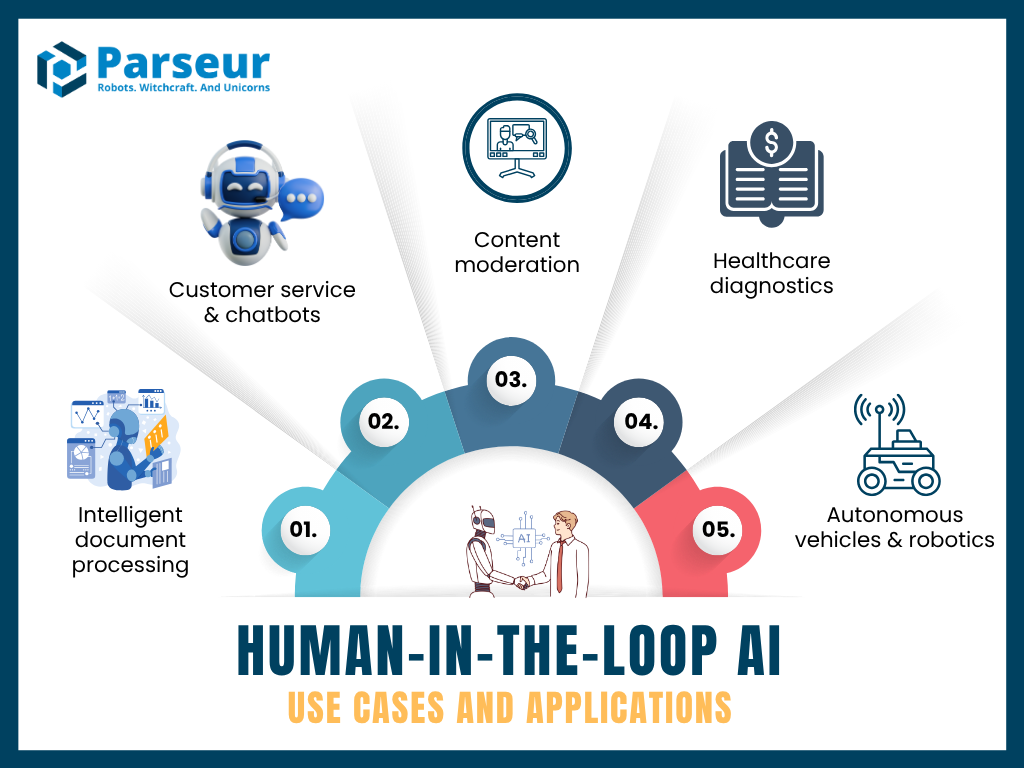
- HITL Platform Features:

Related Terms
- Human-on-the-loop
- Human-out-of-the-loop
- Feedback loop
- Model drift
- Edge cases
- Explainable AI (XAI)
- RLHF (Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback)
Explore More
For a deep dive, review the comprehensive guides, best practices, and real-world case studies linked above. These resources provide up-to-date, authoritative insights into building, scaling, and governing effective Human-in-the-Loop AI systems.
Related Terms
Active Learning
Active learning is a machine learning approach where algorithms actively select the most informative...
Thinking Systems
AI models that spend more computation time on reasoning before generating responses for improved acc...
Data Augmentation
A technique that creates new training examples by modifying existing data, helping AI models learn b...
Few-Shot Learning
A machine learning approach that enables AI models to learn and adapt to new tasks using only a few ...
AI Implementation
AI Implementation is the process of integrating artificial intelligence tools and systems into a bus...
AI Reporting
AI Reporting is technology that automatically analyzes data from multiple sources and generates clea...
